 At 321 Web Marketing, we were recently conducting interviews for an open CMO position. To our dismay, not one candidate could accurately answer the question, ‘What is the PageRank algorithm?’
At 321 Web Marketing, we were recently conducting interviews for an open CMO position. To our dismay, not one candidate could accurately answer the question, ‘What is the PageRank algorithm?’
For a digital marketing agency, not understanding PageRank is a significant shortfall, as it is essential for effective marketing and search engine optimization strategies.
Can your digital marketing provider answer this question?
“What Is The PageRank Algorithm?” The Simple Answer
PageRank, developed in 1996, is Google’s proprietary method for determining a web page’s significance based on its inbound links. Simply stated, this can be compared to a voting system; each link to a page acts like a vote of confidence—pages with more votes, especially from trusted sources, are viewed as more valuable.
Based on the example used within the video above, let’s consider a game of soccer where players pass the ball to teammates—the more passes a player receives from skilled teammates, the more they are viewed as essential to the team’s broader success. Similarly, a webpage gains authority when reputable sites link directly to it—and the more links, the better.
Although Google’s algorithms have evolved significantly since PageRank’s initial introduction, this concept remains foundational in SEO. It continues to influence how Google evaluates website relevance and authority today, actively shaping search results to highlight the most valuable content.
How PageRank Impacts Search Results
PageRank plays a fundamental role in deciding precisely where your website appears in Google’s search results. It measures the importance of your pages based on the quality and quantity of links they receive.
Pages with strong links from high-authority websites are more likely to rank higher, as those links act like endorsements, signaling their trust and overall relevance. High-quality links carry more weight than a large number of low-value ones; a link from a reputable site such as a news outlet or respected industry blog holds much more influence than links from unrelated or spammy websites.
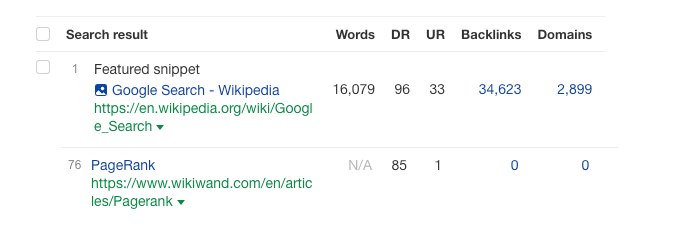
As of 12/12/24, the #1 search result for “PageRank” is owned by Wikipedia within a featured snippet. In Figure 1.1, we are able to see a visualization of PageRank itself in action. The Wikipedia page for PageRank has 2,899 different websites and an overall total of 34,623 backlinks linking back to their page. Whereas WikiWand’s PageRank page does not have any domains or backlinks linking to their page. Even though WikiWand has a slightly lower Domain Authority score (85) compared to Wikipedia (96), WikiWand ranks #76 for the keyword “PageRank”.
While PageRank is just one of the hundreds of ranking signals Google uses today, it laid the foundation for modern algorithms and introduced the idea of evaluating link quality and relevance—concepts still central to SEO.
Important Factors Which Influence PageRank
Several factors directly influence your PageRank, and understanding the differences between them can guide you toward strategies that elevate your site’s SEO performance. Each factor plays a distinct role in signaling value and relevance to Google.
Volume & Quality of Backlinks
 The number of backlinks your site receives does matter, but quality always outweighs quantity. A link from a respected industry leader holds far more weight than dozens from unrelated or low-quality sources.
The number of backlinks your site receives does matter, but quality always outweighs quantity. A link from a respected industry leader holds far more weight than dozens from unrelated or low-quality sources.
For instance, a link from a trusted news source can substantially improve your PageRank, whereas links from low-quality directories could negatively affect it. With this in mind, focus on earning links from authoritative sites that genuinely find your content valuable.
Anchor Text
Anchor text, the clickable text in a hyperlink, connects your page to specific keywords or topics. When properly implemented, it aids Google in understanding how your content relates to a given search query.
For example, a link with the text “Reddit marketing tips” is more effective than generic phrases like “click here.” Relying too heavily on exact-match anchor text can appear manipulative, potentially attracting penalties—instead, taking a diverse and natural approach works best.
Links With Higher Click Potential
Google understands that some links are likelier to be clicked and adjusts their results accordingly. Links prominently placed in the main content of a page carry more value than those buried in footers or sidebars.
Think about user behavior—links naturally integrated into engaging content are more likely to get clicked and pass meaningful PageRank.
Internal Linking
Internal links serve a dual purpose: guiding users through your site and distributing PageRank across your pages. A well-structured internal linking strategy can bring visibility to pages that might otherwise go unnoticed.
For example, linking a useful internal PDF/resource or a high-authority blog post to a newer page gives it a boost in both traffic and ranking potential.
NoFollow Links
 Originally designed to prevent the transfer of PageRank, nofollow links now function as “hints” rather than strict barriers. Google may still consider these links when evaluating your site.
Originally designed to prevent the transfer of PageRank, nofollow links now function as “hints” rather than strict barriers. Google may still consider these links when evaluating your site.
While they are less influential than do-follow links, nofollow links add authenticity to your backlink profile. A natural mix of nofollow and do-follow links demonstrates an organic linking strategy, which Google rewards over manipulative tactics.
Want To Improve Your Positioning In Search Results?
Understanding page rank is essential for building a strong SEO strategy since it influences how Google evaluates your site’s authority and relevance, which directly impacts your search rankings. Focusing on quality backlinks, thoughtful internal links, and content that serves users can achieve much better results in your optimization efforts.
Transform your website’s performance today—schedule a consultation with 321 Web Marketing now. Our team can help you optimize your PageRank and boost your overall visibility in those ever-important Google search results.

